Optimizing your manufacturing process is about more than just moving faster. It's a deep-dive discipline focused on making your facility more efficient, boosting quality, and building operational resilience from the ground up. In the world of food-grade and programmatic fulfillment, this takes on a whole new meaning. It's about weaving safety, compliance, and mission impact into every kit, meal, and delivery you send out the door.
Optimizing Your Food-Grade Manufacturing Foundation
Let's get real and move beyond generic theories. In the high-stakes environment of government food programs and specialized logistics, "manufacturing process optimization" isn't a corporate buzzword—it's the very bedrock of your operation.
Of course, core principles like Lean Manufacturing and Six Sigma offer a great starting point, but they need some serious rethinking when you're dealing with the unique pressures of this sector. A standard factory might obsess over reducing machine downtime, but your reality is far more complex.
You're juggling strict allergen segregation protocols, maintaining cold-chain integrity for temperature-sensitive WIC items, and assembling intricate kits for programs like the Child and Adult Care Food Program (CACFP). Here, a single process failure doesn’t just hit your profit margin; it can compromise food safety, trigger a federal compliance violation, or mean failing an entire community in need.
Adapting Core Principles for Mission-Driven Work
Traditional optimization is all about cutting waste and reducing variation. But for you, "waste" isn't just a pallet of extra inventory. It's a box of senior meals packed with the wrong nutritional components or a shipment of milk that sat on the loading dock for too long.
"Variation" isn't a slightly off-spec part from a machine. It's a gluten-free kit that was accidentally cross-contaminated with an allergen. This is exactly why a one-size-fits-all manufacturing playbook just won't cut it. Your optimization journey has to be built on a foundation that puts these three things first:
- Safety First: This means rigorous controls for allergen handling, meticulous lot tracking for recalls, and unwavering adherence to FDA food-grade storage requirements.
- Compliance Always: Your processes must be designed from the start to meet the specific, non-negotiable demands of the USDA, SFSP, or Buy American provisions.
- Impact-Driven Efficiency: Workflows should be built to get the right food to the right people at the right time, all while maximizing the value of every single dollar.
To better frame this, let's look at how the core pillars of optimization transform when applied to the unique challenges of food-grade and programmatic logistics.
Core Optimization Pillars for Food-Grade Fulfillment
| Pillar | Traditional Definition | Food-Grade & Programmatic Application |
|---|---|---|
| Waste Reduction (Muda) | Eliminating non-value-added activities like excess inventory, unnecessary motion, and overproduction. | Preventing spoilage from temperature excursions, minimizing errors in kit assembly that lead to rework, and avoiding ingredient cross-contamination. |
| Process Standardization | Creating consistent, repeatable steps for every task to ensure predictable quality and output. | Documenting and enforcing allergen segregation protocols, standardizing kitting lines for different programs (e.g., CACFP vs. SFSP), and creating uniform receiving procedures for lot tracking. |
| Continuous Improvement (Kaizen) | Empowering teams to identify and implement small, ongoing improvements to the workflow. | Regularly reviewing pick paths to reduce travel time for temperature-sensitive items, getting feedback from volunteers to make kitting stations more ergonomic, and refining WMS rules to flag near-expiry products earlier. |
| Quality at the Source (Jidoka) | Building quality checks into the process so that defects are caught and addressed immediately. | Implementing barcode scanning at each stage to verify correct components, using temperature monitoring alerts in storage, and training staff to spot and quarantine compromised packaging instantly. |
This table illustrates that while the foundational concepts are the same, their real-world application in our sector is worlds apart. It's a shift from a purely economic focus to one that is driven by safety, compliance, and the well-being of the people we serve.
From Raw Ingredients to Final Delivery
Think about the entire lifecycle of a programmatic order. The journey begins with compliant sourcing, moves through allergen-aware receiving and storage, and then flows into kitting and assembly. Every single one of these steps is a ripe opportunity for optimization.
For instance, are your kitting lines designed to minimize movement and strain for volunteers? Are your pick-and-pack workflows configured in your WMS to automatically flag lots that are nearing their expiration date?
The process doesn't end until the final package is sealed. The choices you make here are absolutely crucial for protecting the contents and communicating vital information. As you tune your efficiency, understanding the nuances of a proper private label packaging setup can prevent a mountain of costly errors and ensure your kits meet all programmatic branding and informational requirements. Every label, box, and seal plays a role in your overall operational integrity.
A key insight from the field is that the most successful food-grade operations don't just copy traditional manufacturing tactics. Instead, they embed compliance and safety checks into the efficiency-building process itself, making them inseparable components of the workflow rather than afterthoughts.
Integrating Technology for Flawless Operations
In food-grade and programmatic fulfillment, technology isn't just a helpful tool; it's the central nervous system that keeps every moving part in sync. Relying on manual entry, paper-based tracking, and inventory guesswork is more than just inefficient—it’s a direct threat to safety, compliance, and the success of your entire mission. To truly get your manufacturing process right, you need a single, reliable source of truth.
This is where integrating Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) and a Warehouse Management System (WMS) becomes non-negotiable. Think of EDI as the automated messenger and the WMS as the operational brain. When they work together, they virtually eliminate the human error that plagues manual systems, ensuring pinpoint accuracy from the moment an order is placed to its final delivery.
The Power Duo: EDI and WMS Integration
EDI is essentially the digital handshake between you and your partners. It’s an automated feed that sends critical information—orders, invoices, shipping notices—directly into your systems without a single person needing to touch a keyboard. The magic happens when that data flows seamlessly into your WMS, which then uses it to direct every single action on the warehouse floor.
This synergy completely transforms your operations. Here's how:
- Wipes Out Manual Entry Errors: By cutting out manual data entry, you dramatically reduce the risk of typos, incorrect quantities, or shipping to the wrong address. For time-sensitive food programs, these kinds of mistakes can be catastrophic.
- Creates Live Inventory Visibility: The second an EDI order hits, the WMS allocates the necessary inventory. This gives you a live, completely accurate picture of what you have and exactly where it is at all times.
- Automates Complex Workflows: You can build rules directly into your WMS to handle specific programmatic needs, like automatically telling your team to pick lots with the nearest expiration date first.
Imagine a state agency sends an EDI feed for its diabetes grocery program. In seconds, the WMS can receive the order, verify that all required items are in stock, generate an optimized pick list based on the warehouse layout, and assign it to a team member. You simply can't achieve that level of speed and accuracy with spreadsheets and clipboards.
This flow chart really breaks down the core focus areas for optimizing your operations. It all starts with safety and compliance—they're the foundation for achieving maximum impact.
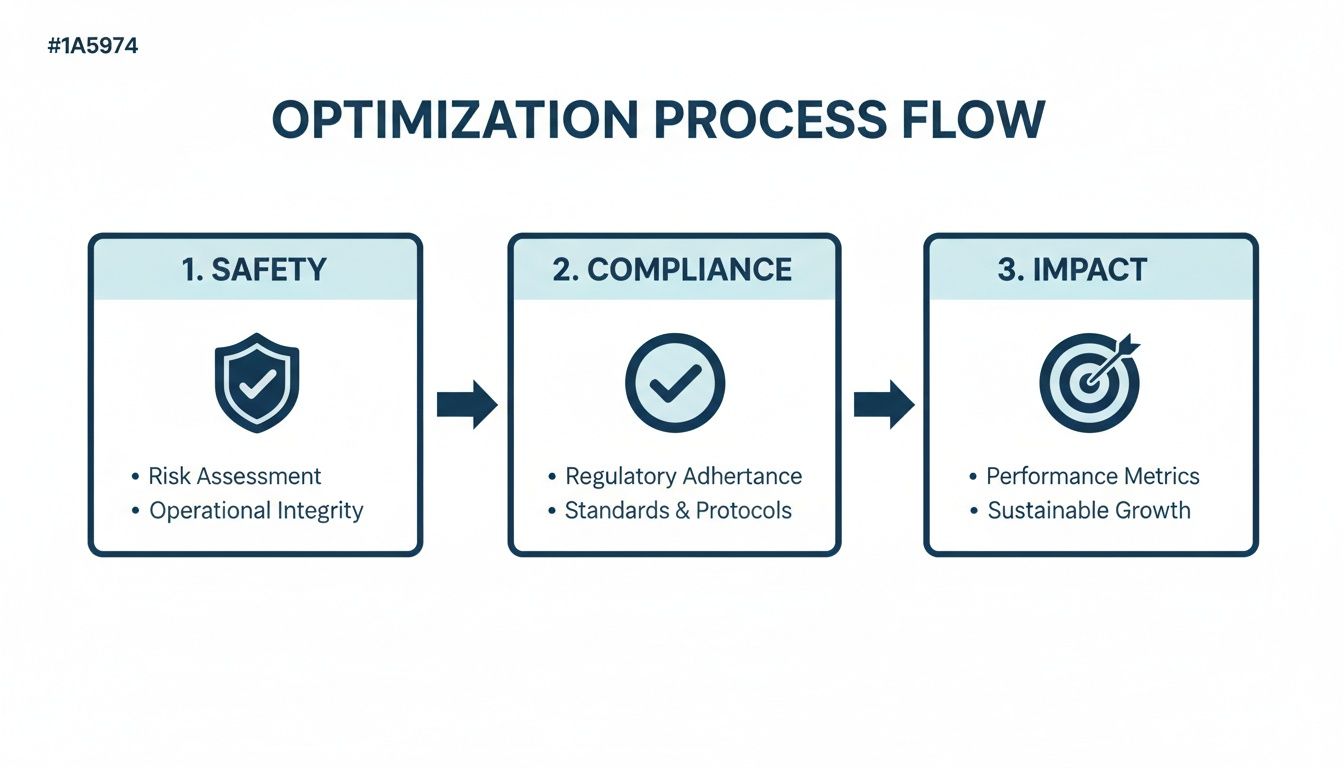
As you can see, operational excellence isn't about a single fix. It's a continuous cycle where safety protocols and compliance checks have to come first before you can get to the meaningful results.
Technology as Your Best Defense
Beyond the day-to-day efficiencies, this kind of tech integration is your best defense when things inevitably go wrong. In the world of food fulfillment, compliance and traceability are everything.
Let's walk through a recall scenario. A manufacturer issues a recall for a specific lot number of canned goods you've already distributed across multiple programs. Without an integrated WMS, you'd be launching a frantic, manual search through piles of paper records, just hoping you can piece together where every single case went. It’s a slow, error-prone process that puts people at risk.
But with a WMS, the response is immediate and precise. You just query the recalled lot number. The system instantly spits out a report showing every kit, pallet, and shipment that contained that specific lot, right down to its final destination. You can notify the right partners in minutes, not days.
This capability isn't just a "nice-to-have"—it's a critical part of modern food safety and a firm requirement for many government contracts. At the heart of this integration is often a robust ERP system in manufacturing, which can tie WMS, EDI, and other functions together into one unified command center.
Ultimately, integrating technology for manufacturing process optimization is about building an operation that is resilient, scalable, and bulletproof on compliance. It ensures every action is traceable, every inventory count is accurate, and every order is fulfilled exactly as required. It gives you the confidence to focus on your mission.
Mastering Your Kitting and Assembly Workflows
Kitting and assembly is where your program's mission gets real. This is the moment individual components become the vital meal boxes, senior kits, or disaster relief packages your community depends on. When we talk about manufacturing process optimization here, it’s not just about speed. It’s about precision, safety, and creating a workflow so intuitive that a first-time volunteer can step in and nail it.
The whole process starts long before the first item ever gets placed in a box. It begins with the physical design of the kitting line. A clunky, poorly designed line is a recipe for bottlenecks, mistakes, and even physical strain on your team. The end goal should always be a seamless, logical flow from raw components to finished, palletized goods ready to ship.

Designing for Error-Proof Efficiency
A truly efficient assembly line is all about minimizing wasted motion. Think about the ergonomics at every single station. Are components within easy reach? Are the heavier items positioned so they can be slid instead of lifted? Every single second you shave off by eliminating an unnecessary step or reach adds up to massive productivity gains over a full shift.
When it comes to preventing mistakes, visual aids are your best friend. Don’t ever rely on memory or complicated written instructions, especially when the pace picks up or you're working with a volunteer crew. Simple, clear visual cues make all the difference.
- Color-Coded Bins: Assign brightly colored totes to different components. This makes identification instant and almost subconscious.
- Picture-Based Instructions: Post large, clear photos at each station showing exactly what the kit should look like at that specific stage.
- Physical Templates: Create a "model box" or a physical template that shows the correct placement for every item. This gives packers a quick, tangible reference for quality control.
These are low-cost, high-impact strategies that dramatically reduce the mental effort required from your team, letting them focus on working quickly and accurately.
The most common point of failure in kitting isn't speed; it's sequence. An operator grabbing items in the wrong order can throw off the entire line. Well-designed visual guides and workstation layouts solve this problem before it starts.
Managing Allergen Segregation and Special Handling
For any food-grade operation, process optimization takes on a critical new dimension: safety. Cross-contamination isn't just a mistake; it's a danger. Your workflows have to be built from the ground up to prevent it, especially when you’re assembling kits with specific dietary needs like gluten-free or peanut-free boxes.
The gold standard here is physical segregation. If you have the space, dedicate separate assembly lines or schedule production runs on different days for kits containing major allergens. If you absolutely have to share a line, your Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) must include a rigorous, fully documented cleaning and sanitization process between every single run. No exceptions.
This same level of discipline applies to anything requiring special handling. Take multi-day CACFP kits that include milk, for example. The cold chain is everything. Your kitting process should be designed so that refrigerated items are the very last components added to the box—right before it’s sealed and moved directly into cold storage or a reefer truck. This minimizes the time those sensitive items spend in the temperature "danger zone." The most successful kitting programs don't treat these safety protocols as an afterthought; they're baked directly into the workflow, making them a natural and non-negotiable part of the job.
A Real-World Disaster Response Scenario
Imagine the call comes in: you need to assemble 5,000 emergency meal kits for a disaster response. And they have to be ready in 24 hours. This is where a well-oiled process doesn't just save money—it saves lives.
In a situation just like this, our team was able to hit the target by activating a pre-designed "surge" kitting line. We used a simple U-shaped layout to maximize the use of our space and keep movement to a minimum. Volunteers were assigned to very specific, single-task stations—one person adds canned protein, the next adds starches, the next adds fruit, and so on.
The keys were clear visual aids and pre-staged components. Before the first volunteer even walked through the door, we had pallets of each item placed at their point-of-use along the line. This completely eliminated the chaos of people hunting for supplies. By standardizing the workflow and making each step simple and repeatable, we built a high-speed, low-error system that met that critical deadline. That’s the real power of an optimized workflow.
Navigating Compliance and Cold Chain Integrity
In food logistics, compliance isn't just about ticking boxes—it's your license to operate. Get it wrong, and you're looking at failed audits, rejected shipments, and a catastrophic breach of public trust. True manufacturing process optimization means weaving regulatory adherence and safety protocols into the very fabric of your workflow, from the receiving dock to the final doorstep.
This becomes especially critical when you're dealing with government contracts and serving vulnerable populations. The rules are strict, and there's no room for error. If you're working on federal programs, for instance, you have to contend with the Buy American provisions, which require a specific percentage of your food products to be sourced and made domestically. That’s not a final check; it's a filter that needs to be applied to your entire procurement and inventory system from the start.
Similarly, programs like the SFSP (Summer Food Service Program) for Rural Non-Congregate delivery involve a mountain of specific documentation. Every single kit has to be traceable, and every delivery logged with absolute precision. A powerful WMS is your best friend here, capturing data automatically at every touchpoint to create a clean, auditable trail.

Upholding the Unbroken Cold Chain
Beyond the paperwork, the physical integrity of your product is everything, particularly for perishables. The cold chain is the fragile sequence of refrigerated production, storage, and distribution. A single break can render an entire shipment unsafe and worthless.
It all starts the moment a reefer truck backs up to your loading dock. An optimized receiving process includes immediate temperature checks before a single pallet is unloaded. Real-time temperature monitoring devices aren't a luxury anymore; they're essential. This data must be logged in your WMS against the specific lot number, creating an unbroken temperature history from the very beginning.
That vigilance has to follow the product through storage and all the way into the final mile. For last-mile delivery—especially for programs serving WIC participants or homebound seniors—the packaging itself becomes a critical control point.
- Insulated Liners: High-quality insulated box liners are your first line of defense, capable of maintaining temperature for hours.
- Gel Packs: You need the right number and size of frozen gel packs, calculated based on package volume, ambient temperature, and expected transit time. Guesswork isn't an option.
- Temperature Indicators: For the most sensitive shipments, simple, single-use temperature indicators give the recipient clear visual proof that the cold chain held firm.
A simple but powerful optimization I've seen work wonders is redesigning the packing station so that refrigerated or frozen items are picked last. This one change minimizes the time these sensitive products are out of their temperature-controlled environment before being sealed for shipment.
Integrating Safety and Compliance into Every Step
A safe operation is an efficient and compliant one. To get through the complex web of food-grade regulations, you have to understand and follow standards like the Australian Workplace Safety Standards. While rules vary by region, the core principles of risk assessment, proper material handling, and documented procedures are universal.
Take FDA food-grade storage requirements. They dictate everything from pest control to the physical separation of raw and ready-to-eat foods. This means your warehouse layout and picking paths must be designed to enforce these rules, creating designated zones for allergens, ensuring proper cleaning space, and building workflows that eliminate any chance of cross-contamination.
Ultimately, compliance and cold chain management aren't just tasks on a checklist. They are the very foundation of an optimized system. By weaving these requirements into your technology, workflows, and physical layout, you build an operation that's not just efficient but also resilient, scalable, and fundamentally safe. To see how these principles come together in the real world, take a look at some of the end-to-end logistics and fulfillment solutions we've put into action.
Using Data to Drive Continuous Improvement
You can’t improve what you don’t measure. In food fulfillment, this isn’t just some business cliché; it’s the principle that separates struggling operations from truly effective ones. Real manufacturing process optimization is built on a foundation of solid data, pushing past the vanity metrics to focus on the numbers that genuinely impact your mission and your bottom line. The goal is to turn the raw data from your Warehouse Management System (WMS) into smarter, faster decisions on the floor.
Forget about those overwhelming dashboards cluttered with dozens of charts. To get started, you need to zero in on the vital few metrics that tell the most important stories about your operation’s health. These KPIs are your pulse, giving you a clear, immediate signal of what's working and—more importantly—where things are starting to break down.
The KPIs That Actually Matter
For the specialized world of food-grade and programmatic fulfillment, three core KPIs provide a powerful starting point. These metrics cut right through the noise, offering actionable insights into quality, timeliness, and cost-efficiency.
-
Order Accuracy Rate: This is your ultimate measure of quality. It’s the percentage of orders shipped with zero errors—no wrong items, no incorrect quantities, no damaged goods. In our world, a mistake isn't just an inconvenience; it can mean a family with specific dietary needs gets the wrong food. A high accuracy rate, tracked directly from WMS scan data, is proof that your processes are reliable.
-
On-Time Shipping Rate: This KPI is all about your ability to meet commitments. It tracks the percentage of orders that leave your facility on or before the promised ship date. For time-sensitive programs, like SFSP meal deliveries or disaster response efforts, shipping on time is simply non-negotiable.
-
Cost Per Kit: Think of this as your efficiency benchmark. You calculate it by dividing the total operational cost of a kitting run (labor, materials, overhead) by the number of completed kits. Tracking this helps you see the real-world impact of process changes and pinpoint which assembly lines are the most cost-effective.
Simply tracking these KPIs isn't enough. The real value comes from setting up simple, visual dashboards that let you spot trends and anomalies at a glance. A sudden dip in your Order Accuracy Rate, for example, is an immediate red flag that a specific process or workstation needs a closer look.
Turning Data into Actionable Insights
With these core metrics in place, you can start asking the right questions to drive continuous improvement. Your data holds the answers, pointing you directly toward the biggest opportunities for optimization. For instance, if your dashboards show a bottleneck on a specific kitting line, you can drill down into the data. Is the delay from slow component replenishment? An ergonomic issue at a workstation? Or are you just understaffed on that line?
This data-driven approach is also invaluable for forecasting. By analyzing historical order volumes from your WMS, you can accurately predict your labor needs for seasonal spikes, like the surge in demand for summer meal programs. Instead of guessing how many volunteers or temporary staff you'll need, you can build a data-backed staffing plan. This prevents overspending and ensures you can meet demand without any last-minute scrambling. This is how you transform raw numbers into a strategic asset for manufacturing process optimization.
Theory is one thing, but putting it into practice is where manufacturing process optimization really shows its teeth. Abstract ideas about efficiency and compliance only come to life when they’re tested by real-world pressure. Let's walk through how these concepts play out in three distinct, high-stakes situations.
These aren't just simple textbook examples. They show the complex dance between technology, workflow design, and the strict rules that come with programmatic fulfillment.
Scenario One: A CACFP Milk Delivery Program
Imagine a CACFP sponsor has to get a new program off the ground, delivering milk to 200 different childcare sites. The logistical challenge is massive. They have to guarantee cold chain integrity across a bunch of different routes while keeping perfect compliance documents for every single delivery.
First, they map the process. They chart the entire journey from the moment milk hits their warehouse dock to the final drop-off. Right away, a huge bottleneck jumps out: the manual verification and logging of temperatures at each site. It’s slow, it’s a magnet for human error, and it puts their compliance in serious jeopardy.
The fix? A tech-forward approach. They arm their delivery drivers with handheld scanners and temperature probes that talk directly to their WMS.
- At the Warehouse: Every case of milk is scanned out, tying its specific lot number to a delivery route.
- At Each Site: The driver simply probes the milk to get a temperature reading. When they scan a site-specific barcode, the system automatically logs the temperature, timestamp, and GPS location.
This one change completely transformed their operation. It got rid of the manual paperwork, created an instant, auditable digital trail for CACFP, and gave them real-time eyes on the entire delivery process.
Scenario Two: A WIC Online Ordering Pilot
A state WIC agency wants to run a pilot program for online ordering. The target audience is participants in a rural area who don’t have easy access to grocery stores. The goal is to make life easier for them while ensuring they can only buy WIC-approved items.
The key to their optimization strategy is a rock-solid integration between their e-commerce platform and their 3PL partner's WMS. This connection creates real-time inventory awareness. Now, the online portal only shows items that are actually on the shelf, which stops the frustration of getting an "out of stock" notice after you've already placed an order.
The most crucial tweak was building rules for inventory-aware substitutions. If a specific brand of 1% milk isn't available, the system is smart enough to suggest a nutritionally identical 1% milk from another approved brand. But it will never, ever offer whole milk as a substitute.
By hard-coding WIC compliance directly into the workflow, they slashed the potential for errors and made the whole shopping experience feel seamless. Every single order that leaves the warehouse is guaranteed to meet the program's strict guidelines without needing a human to double-check it.
Scenario Three: A 72-Hour Disaster Response
An emergency manager is on the hook for planning a rapid, 72-hour disaster response. This means getting thousands of ready-to-eat meal kits assembled and out the door. In this world, speed and accuracy are everything.
Their entire strategy is built on pre-planning and smart workflow design. They don't wait for a disaster to figure out their kitting line. Instead, they create pre-configured "surge" line setups, complete with standardized workstations and simple, picture-based instructions that anyone can follow.
The moment a disaster is declared, the plan kicks into gear. Pallets of pre-selected, shelf-stable food are moved to designated markings on the floor. Volunteers are assigned single, repetitive tasks—one person adds the protein, the next adds the fruit, and so on down the line. This assembly-line model cuts training time to almost zero and pushes throughput to the max.
By standardizing the process long before it's needed, they can scale up at a moment's notice, creating a high-speed, low-error system built to perform under the most intense pressure.
Common Questions and Straight Answers
When you're knee-deep in operations, questions are going to pop up. Here are some of the most common ones we hear from food banks and nutrition programs, along with our direct, no-nonsense answers.
We're a Smaller Food Bank. How Do We Start Optimizing Without a Big Budget?
Forget the expensive tech for a moment. Just start by mapping out a single, core process. Grab a whiteboard and chart out every single step it takes to pack a senior box or handle a new donation delivery.
This simple act is incredibly powerful. It almost always shines a light on obvious bottlenecks or steps that just don't make sense anymore. You might find that reorganizing a storage area to improve the flow of volunteers or creating a simple, laminated checklist for kitting stations can make a world of difference—all for next to no cost.
The goal is to get a quick, meaningful win. Perfecting your volunteer kitting process is a fantastic first step and builds momentum for bigger changes down the road.
What's the Single Most Important Piece of Tech for Scaling a Nutrition Program?
It has to be a robust Warehouse Management System (WMS). While lots of tools can help, a good WMS is the operational brain of your entire facility. It’s the foundational layer that makes true optimization possible.
A WMS gives you that crucial real-time view into your inventory, makes sure orders are picked correctly, and handles the essential lot tracking that's non-negotiable for food safety. Everything else you do to scale and improve efficiency will ultimately be powered by the data and control your WMS provides.
How Should We Handle Substitutions for an Online WIC Order?
This is a classic challenge that needs a smart mix of technology and clear, upfront rules. First, you absolutely need an inventory-aware WMS that’s connected to your ordering platform. This prevents people from ordering items you don't actually have in stock.
For the substitutions themselves, you have to define the rules of engagement beforehand, based on nutritional equivalency and program guidelines. For example, you might create a rule that allows 1% milk to be substituted for 2% milk, but never for whole milk.
The final piece is communication. Be completely transparent about your substitution policy during the checkout process. This sets the right expectations from the get-go and avoids any frustration or disappointment when the order arrives.
At Umoja Health, we live and breathe this stuff. We specialize in designing and managing compliant, efficient food programs that make a real impact. If you're ready to take your operations to the next level and scale your mission, see how we can help at Umoja Health Solutions.

